Insurance paid in advance is an asset that represents the value of insurance coverage that has been paid for but not yet used. For example, if you pay your car insurance policy for the entire year upfront, the portion of the premium that covers the period after the current month is considered an asset.
Insurance paid in advance is important because it provides a cushion against unexpected financial losses. If you have to file a claim, the insurance company will use the funds from your prepaid premium to cover the costs of the claim. This can help you to avoid having to pay out-of-pocket expenses, which can be a significant financial burden.
There are several benefits to paying your insurance premiums in advance. First, it can help you to save money. Many insurance companies offer discounts for customers who pay their premiums annually or semi-annually. Second, it can help you to avoid late payment penalties. If you forget to pay your premium on time, you may be charged a late payment fee. Third, it can help you to protect your credit score. Late payments can damage your credit score, which can make it more difficult to get approved for loans and other forms of credit.
If you are considering paying your insurance premiums in advance, it is important to compare the costs and benefits of doing so. You should also make sure that you have enough money to cover the cost of the premium, as well as any other expenses that may arise.
Insurance Prepaid as an Asset
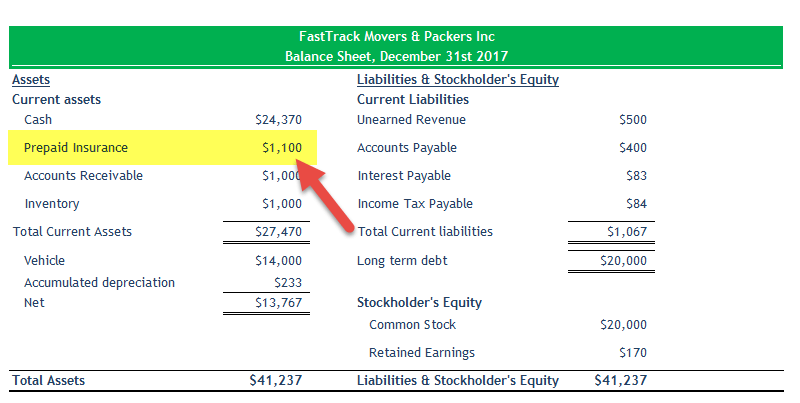
Insurance paid in advance can be categorized as a current asset, specifically a prepaid expense, on the balance sheet of a company. It represents the portion of insurance coverage that has been paid for but not yet utilized.
- Definition: A prepayment for future insurance coverage.
- Classification: Current asset, prepaid expense.
- Recognition: Recorded as an asset when the premium is paid.
- Expense recognition: Recognized over the period of insurance coverage.
- Financial impact: Improves the current ratio and working capital.
- Tax implications: May be deductible as a business expense.
- Internal control: Proper documentation and reconciliation of insurance policies and payments are crucial.
Understanding these key aspects is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. Prepaid insurance reduces the current year’s insurance expense and improves the company’s financial ratios. It also provides a buffer against unexpected claims and ensures continuous coverage. Proper management of prepaid insurance is crucial for effective cash flow management and maintaining a strong financial position.
Definition
This definition captures the essence of “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” by highlighting that insurance paid in advance represents a payment made for future insurance coverage. It is a crucial component of understanding the concept because it establishes the connection between the asset and the underlying insurance policy.
The prepayment for future insurance coverage is recorded as an asset because it provides the company with a future economic benefit. The insurance policy guarantees coverage for a specific period, and the prepaid premium secures that coverage. In the event of an insured event, the insurance company will use the funds from the prepaid premium to cover the costs of the claim. This provides the company with financial protection against potential losses.
Understanding the definition of insurance paid in advance as a prepayment for future insurance coverage is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. It allows companies to properly recognize and value this asset on their balance sheets. This, in turn, provides stakeholders with a clear picture of the company’s financial position and risk exposure.
Classification
The classification of insurance paid in advance as a current asset, specifically a prepaid expense, is a crucial aspect of understanding “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa”. This classification has several important implications:
- Short-term asset: Prepaid insurance is considered a current asset because it is expected to be used or consumed within one year or the company’s operating cycle, whichever is longer. This aligns with the definition of insurance paid in advance as a prepayment for future insurance coverage.
- Expense recognition: The prepaid insurance asset is gradually recognized as an expense over the period of insurance coverage. This is done through a process called amortization, which allocates the prepaid premium to each accounting period that benefits from the coverage.
- Financial statement presentation: Prepaid insurance is typically presented on the balance sheet under the current assets section, usually as a separate line item. This provides transparency to stakeholders about the company’s insurance coverage and its financial position.
- Matching principle: The classification of prepaid insurance as a current asset follows the matching principle of accounting. This principle requires that expenses be recognized in the same period as the revenues they generate. In this case, the prepaid insurance expense is matched to the period in which the insurance coverage is provided.
Understanding the classification of insurance paid in advance as a current asset, prepaid expense, is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. It ensures that the company’s financial statements provide a true and fair view of its financial position and performance.
Recognition
The recognition of insurance paid in advance as an asset when the premium is paid is a fundamental aspect of “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa”. This recognition reflects the accrual accounting principle, which requires that transactions be recorded in the accounting records in the period in which they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
- Initial recognition: When an insurance premium is paid, the full amount is recorded as an asset on the balance sheet. This is because the company has acquired a future economic benefit in the form of insurance coverage, even though the coverage period may extend beyond the current accounting period.
- Expense recognition: Over the period of insurance coverage, the prepaid insurance asset is gradually recognized as an expense. This is done through a process called amortization, which allocates the prepaid premium to each accounting period that benefits from the coverage. Amortization is typically done on a straight-line basis, meaning that the same amount of expense is recognized in each period.
- Matching principle: The recognition of insurance paid in advance as an asset when the premium is paid follows the matching principle of accounting. This principle requires that expenses be recognized in the same period as the revenues they generate. In this case, the insurance expense is matched to the period in which the insurance coverage is provided.
- Financial statement presentation: Prepaid insurance is typically presented on the balance sheet under the current assets section, usually as a separate line item. This provides transparency to stakeholders about the company’s insurance coverage and its financial position.
Understanding the recognition of insurance paid in advance as an asset when the premium is paid is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. It ensures that the company’s financial statements provide a true and fair view of its financial position and performance.
Expense recognition
The expense recognition principle is a fundamental aspect of “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” (insurance paid in advance as an asset). It dictates that insurance expenses should be recognized over the period of insurance coverage, rather than when the premium is paid. This principle ensures that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect the matching of expenses to the revenues they generate.
For example, consider a company that pays an annual insurance premium of $12,000 on January 1st. Under the expense recognition principle, the company would recognize $1,000 of insurance expense each month for the 12-month period of coverage. This is because each month, the company receives the benefit of one-twelfth of the total insurance coverage.
Proper expense recognition is crucial for several reasons. First, it provides a more accurate picture of the company’s financial performance. By recognizing expenses over the period of insurance coverage, the company avoids overstating its income in the period in which the premium is paid. Second, it ensures that the company’s financial statements comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and other accounting standards. Third, it facilitates comparability between companies by ensuring that all companies are recognizing expenses in a consistent manner.
Understanding the connection between expense recognition and “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. It allows companies to properly match expenses to revenues, which provides a more accurate picture of the company’s financial performance and position.
Financial impact
The financial impact of prepaid insurance is a crucial aspect of understanding “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa”. Prepaid insurance improves the current ratio and working capital, which are important indicators of a company’s financial health.
The current ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. Prepaid insurance, as a current asset, increases the numerator of the current ratio, thereby improving the overall ratio. This indicates that the company has sufficient short-term assets to cover its short-term liabilities.
Working capital is the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities. Prepaid insurance, as a current asset, increases the working capital. This indicates that the company has more resources available to fund its operations and meet its financial obligations.
Improving the current ratio and working capital is important for several reasons. First, it enhances the company’s creditworthiness and ability to obtain financing. Lenders and investors view companies with strong current ratios and working capital as less risky and more likely to repay their debts. Second, it provides a buffer against unexpected expenses and financial emergencies. Companies with ample working capital are better equipped to handle unexpected events without resorting to costly financing options.
Understanding the financial impact of prepaid insurance is essential for effective financial management and decision-making. By improving the current ratio and working capital, prepaid insurance contributes to the overall financial health and stability of the company.
Tax implications
Understanding the tax implications of insurance paid in advance is a crucial aspect of “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” (insurance paid in advance as an asset). In many jurisdictions, insurance premiums paid in advance may be deductible as a business expense for tax purposes. This can significantly reduce the cost of insurance coverage for businesses.
- Deductibility: In many countries, insurance premiums paid in advance are considered an ordinary and necessary business expense and are therefore deductible from taxable income. This means that businesses can reduce their tax liability by deducting the cost of insurance coverage.
- Timing of deduction: The timing of the deduction for insurance premiums paid in advance depends on the accounting method used by the business. Under the cash basis method, the deduction is taken in the year the premium is paid. Under the accrual basis method, the deduction is taken over the period of insurance coverage.
- Limitations: There may be limitations on the amount of insurance premiums that can be deducted as a business expense. These limitations vary depending on the jurisdiction and the type of insurance coverage.
Understanding the tax implications of insurance paid in advance can help businesses optimize their tax strategy and reduce their overall cost of insurance coverage. By taking advantage of the deductibility of insurance premiums, businesses can improve their profitability and financial performance.
Internal control
Internal control is a crucial component of “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” (insurance paid in advance as an asset). Proper documentation and reconciliation of insurance policies and payments ensure the accuracy and reliability of the asset account. Without effective internal control, there is an increased risk of errors, fraud, and misstatement of the insurance asset.
Proper documentation provides a clear audit trail of insurance transactions. This includes maintaining records of insurance policies, premium payments, and claims. Regular reconciliation of insurance policies and payments helps to identify any discrepancies or errors. By comparing the records of the insurance company with the company’s own records, any differences can be investigated and corrected promptly.
Effective internal control over insurance paid in advance helps to ensure that the asset is properly valued and disclosed in the financial statements. This, in turn, provides stakeholders with a true and fair view of the company’s financial position and performance. Moreover, it helps to prevent the overstatement or understatement of insurance assets, which can have a material impact on the company’s financial ratios and creditworthiness.
In summary, proper documentation and reconciliation of insurance policies and payments are essential for maintaining the integrity of the insurance asset account. By implementing effective internal control procedures, companies can mitigate the risk of errors, fraud, and misstatement, and ensure the accuracy and reliability of their financial statements.
FAQs on Insurance Paid in Advance as an Asset
The following frequently asked questions provide concise answers to common queries related to insurance paid in advance as an asset:
Question 1: What is insurance paid in advance?
Insurance paid in advance is a prepayment for future insurance coverage. It represents the portion of insurance premiums paid that covers the period beyond the current accounting period.
Question 2: How is insurance paid in advance classified on the balance sheet?
Insurance paid in advance is classified as a current asset, specifically a prepaid expense, on the balance sheet.
Question 3: When is insurance paid in advance recognized as an asset?
Insurance paid in advance is recognized as an asset when the premium is paid.
Question 4: How is the expense for insurance paid in advance recognized?
The expense for insurance paid in advance is recognized over the period of insurance coverage.
Question 5: What are the financial implications of insurance paid in advance?
Insurance paid in advance improves the current ratio and working capital.
Question 6: Are there any tax implications for insurance paid in advance?
In many jurisdictions, insurance premiums paid in advance may be deductible as a business expense for tax purposes.
These FAQs provide a basic understanding of insurance paid in advance as an asset. For more detailed information, please consult a qualified accountant or financial advisor.
Transition to the next article section…
Tips on Managing Insurance Paid in Advance as an Asset
Effectively managing insurance paid in advance can enhance financial reporting accuracy and optimize cash flow. Here are some practical tips to consider:
Tip 1: Establish Clear Documentation and Approval ProceduresMaintain a comprehensive system for documenting insurance policies, premium payments, and claims. Implement clear approval procedures to ensure proper authorization and avoid unauthorized payments.Tip 2: Reconcile Insurance Policies and Payments RegularlyPeriodically reconcile insurance policies and payments with the insurance company’s records. This helps identify discrepancies and errors, ensuring the accuracy of the insurance asset account.Tip 3: Review Insurance Coverage AdequacyRegularly review insurance coverage to ensure it meets the company’s current and future needs. Adjust coverage levels as necessary to avoid underinsurance or overinsurance.Tip 4: Optimize Premium Payment TimingConsider optimizing the timing of insurance premium payments to align with cash flow and minimize unnecessary interest charges. Explore payment plans or discounts for early payments.Tip 5: Leverage Technology for Efficient ManagementUtilize accounting software or other technology tools to automate insurance-related tasks, such as premium payments, reconciliations, and expense recognition. This can improve efficiency and reduce manual errors.Tip 6: Seek Professional Advice When NeededConsult with qualified accountants or insurance professionals for guidance on complex insurance matters, such as the proper classification and valuation of insurance assets.Tip 7: Maintain Strong Internal ControlsImplement robust internal controls over insurance-related transactions to prevent fraud, errors, and misstatement. Establish clear roles and responsibilities, and ensure proper segregation of duties.Summary of Key Takeaways:By following these tips, companies can enhance the management of insurance paid in advance as an asset, ensuring accurate financial reporting, optimizing cash flow, and mitigating risks.Transition to the article’s conclusion…
Conclusion
Insurance paid in advance represents an important aspect of asset management and financial reporting. Understanding its definition, classification, recognition, and expense recognition is crucial for accurate financial statements. The financial impact of insurance paid in advance on the current ratio and working capital should also be considered. Proper internal control procedures ensure the integrity of the insurance asset account. By effectively managing insurance paid in advance, companies can optimize cash flow, mitigate risks, and enhance financial reporting accuracy.
In conclusion, “asuransi dibayar dimuka termasuk aset apa” highlights the significance of insurance paid in advance as a current asset. Proper accounting and management of this asset contribute to the overall financial health and stability of a company.